What Is The Template Of The Pcr
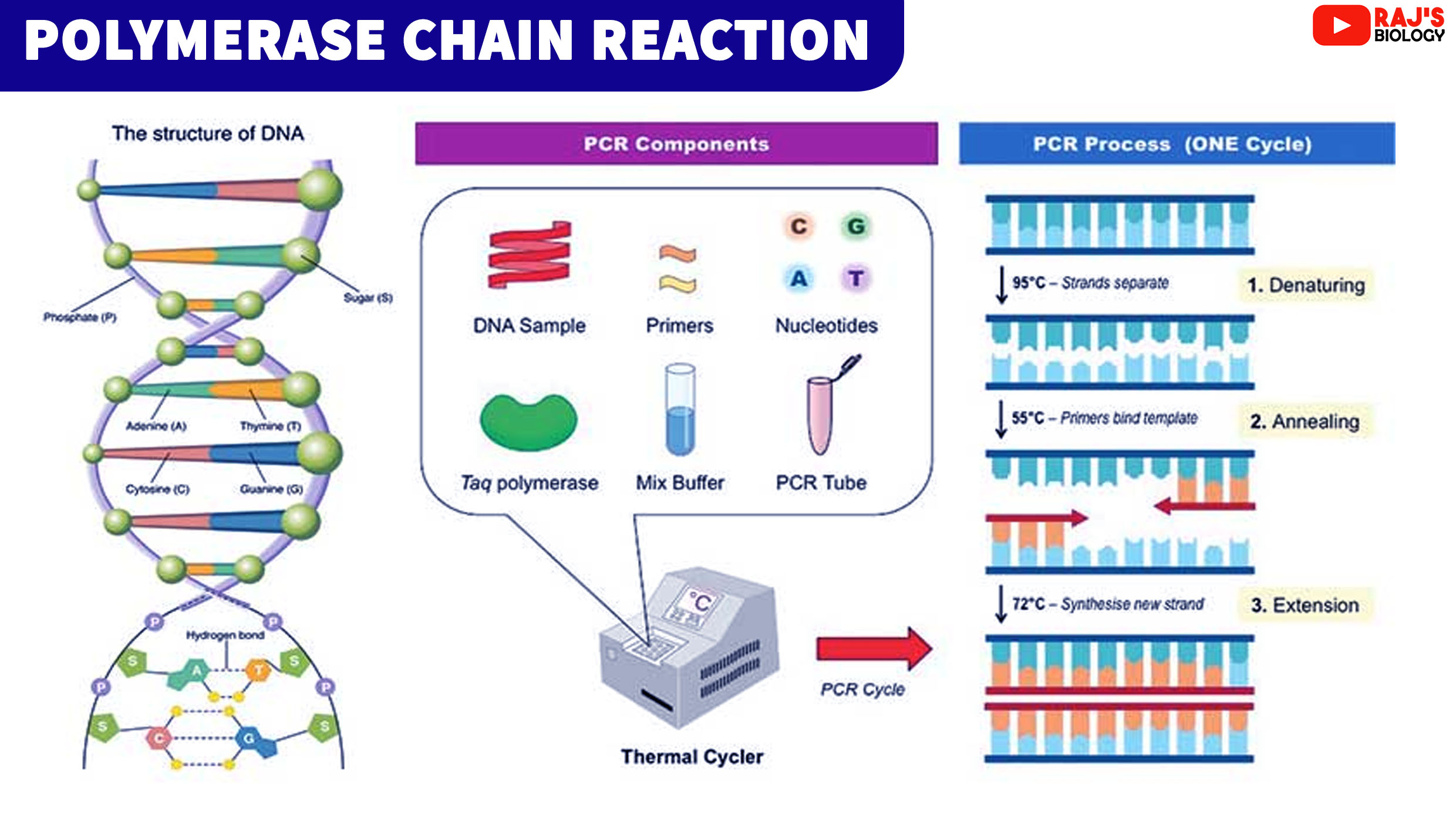
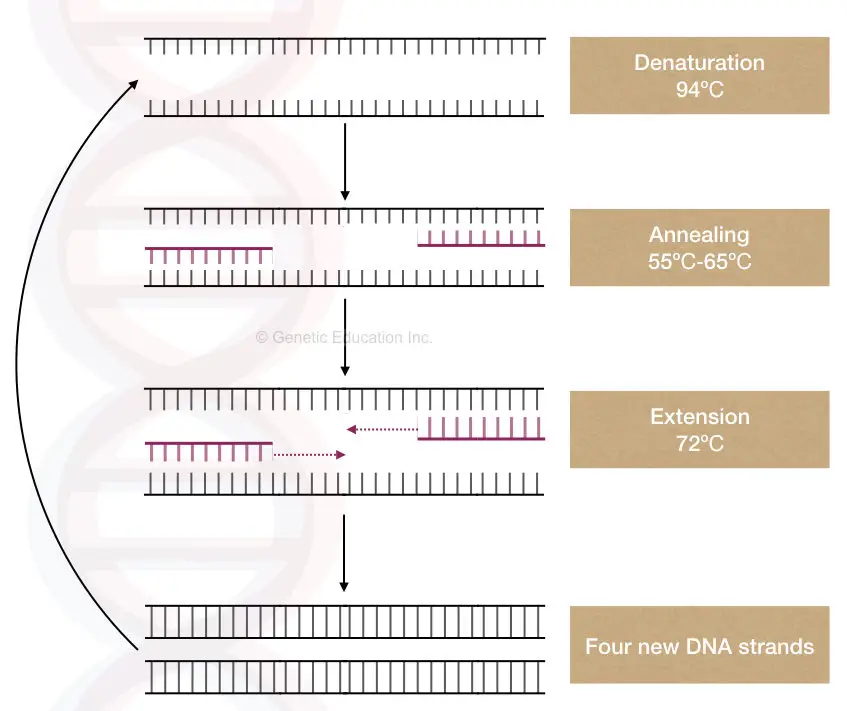
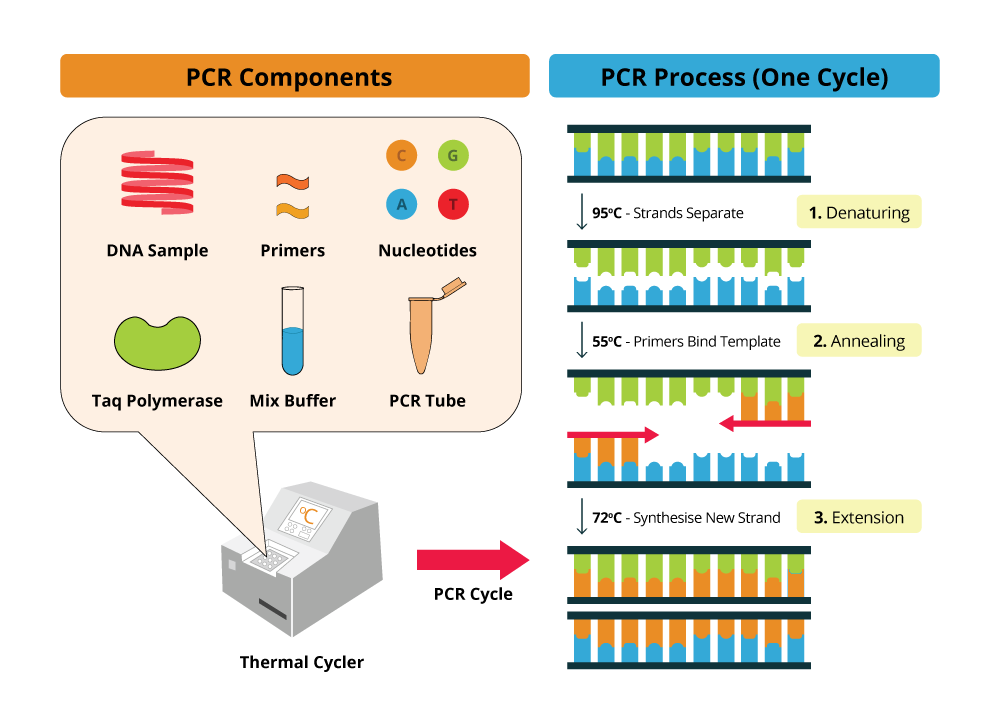
What Is The Template Of The Pcr - Nevertheless, the composition or complexity of the dna contributes to. Web as pcr progresses, the dna generated is itself used as a template for replication, setting in motion a chain reaction in which the original dna template is exponentially amplified. Multiple homologous templates present in copy numbers that vary within several orders of magnitude. Web the pcr technique is based on the natural processes a cell uses to replicate a new dna strand. Web pcr (polymerase chain reaction) is a revolutionary method developed by kary mullis in the 1980s. Web these are typically short, single stranded oligonucleotideswhich are complementary to the outer regions of known sequence. Pcr primers are designed as pairs, referred to as forward and reverse primers. Ways of collecting samples include a nasal swab, a saliva swab, or taking a sample of blood. Add required reagents or mastermix and template to pcr tubes. (b) δrn is rn minus the baseline. This technique was developed in 1983 by kary mullis, an american biochemist. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a laboratory nucleic acid amplification technique used to denature and renature short segments of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) or ribonucleic acid (rna) sequences using dna polymerase i enzyme, an isolate from thermus aquaticus, known as taq dna. Web the high temperature causes. Primers, or oligonucleotides, are short single strands complementary to each dna strand. Web pcr or polymerase chain reaction is a technique used in molecular biology to create several copies of a certain dna segment. Web pcr is a powerful amplification technique that can generate an ample supply of a specific segment of dna (i.e., an amplicon) from only a small. Rn is the fluorescence of the reporter dye divided by the fluorescence of a passive reference dye; I.e.,rn is the reporter signal normalized to the fluorescence signal of applied biosystems™ rox™ dye. Web pcr (polymerase chain reaction) is a revolutionary method developed by kary mullis in the 1980s. Multiple homologous templates present in copy numbers that vary within several orders. Amplify per thermo cycler and primer parameters. Rn is the fluorescence of the reporter dye divided by the fluorescence of a passive reference dye; Web pcr is a powerful amplification technique that can generate an ample supply of a specific segment of dna (i.e., an amplicon) from only a small amount of starting material (i.e., dna template or target sequence).. Rn is the fluorescence of the reporter dye divided by the fluorescence of a passive reference dye; *add mineral oil to prevent evaporation in a thermal cycler without a heated lid. Web pcr is a powerful amplification technique that can generate an ample supply of a specific segment of dna (i.e., an amplicon) from only a small amount of starting. In qpcr, the amount of amplification product is measured in each pcr cycle using fluorescence. The dna polymerase is the key enzyme that links individual nucleotides together to form the pcr product. Web pcr (polymerase chain reaction) is a revolutionary method developed by kary mullis in the 1980s. Web pcr is a powerful amplification technique that can generate an ample. Web a polymerase chain reaction (pcr) test detects genetic material from a pathogen or abnormal cell sample. Pcr has made it possible to generate millions of copies of a small segment of dna. Web in the second pcr step, 183 base pairs amplified by the first pcr step are used as a template. Between the bases in two strands of. Web the key ingredients of a pcr reaction are taq polymerase, primers, template dna, and nucleotides (dna building blocks). Genomic dna, plasmid dna, cdna or purified pcr products can be used as template dna in pcr. The main components of pcr are a template, primers, free nucleotide bases, and the dna polymerase enzyme. The dna polymerase is the key enzyme. The oligonucleotides serve as primers for dna polymerase and each of the denatured strands of the parental dna duplex serves as the template. Rn is the fluorescence of the reporter dye divided by the fluorescence of a passive reference dye; Add required reagents or mastermix and template to pcr tubes. Web the key ingredients of a pcr reaction are taq. Web pcr is a powerful amplification technique that can generate an ample supply of a specific segment of dna (i.e., an amplicon) from only a small amount of starting material (i.e., dna template or target sequence). Web pcr (polymerase chain reaction) is a revolutionary method developed by kary mullis in the 1980s. Add required reagents or mastermix and template to. Such conditions are a breeding ground for chimeras and heteroduplexes. A pcr template for replication can be of any dna source, such as genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna), and plasmid dna. The main components of pcr are a template, primers, free nucleotide bases, and the dna polymerase enzyme. Restriction digest of plasmid dna. This technique was developed in 1983 by kary mullis, an american biochemist. Pcr is based on using the ability of dna polymerase to synthesize new strand of dna complementary to the offered template strand. Between the bases in two strands of template dna to break and the two strands to separate. Only a few biological ingredients are needed for pcr. Web in the second pcr step, 183 base pairs amplified by the first pcr step are used as a template. Web polymerase chain reaction, or pcr, is a laboratory technique used to make multiple copies of a segment of dna. Web enter the pcr template here (multiple templates are currently not supported). The dna template contains the specific region of interest for amplification, such as dna extracted from a piece of hair. The source of dna can include genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna) or plasmids. This results in two single strands of dna, which will act as templates for the production of the new strands of dna. Pcr has made it possible to generate millions of copies of a small segment of dna. Web the key ingredients of a pcr reaction are taq polymerase, primers, template dna, and nucleotides (dna building blocks). A standard polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is an in vitro method that allows a single, short region of a dna molecule (single gene perhaps) to be copied multiple times by taq polymerase. I.e.,rn is the reporter signal normalized to the fluorescence signal of applied biosystems™ rox™ dye. Web pcr is a powerful amplification technique that can generate an ample supply of a specific segment of dna (i.e., an amplicon) from only a small amount of starting material (i.e., dna template or target sequence). Amplify per thermo cycler and primer parameters.Polymerase Chain Reaction Notes Rajus Biology
Fun with Biotechnology PCR
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) template DNA and dsRNA. (A) Diagram
What are the properties of PCR (template) DNA?
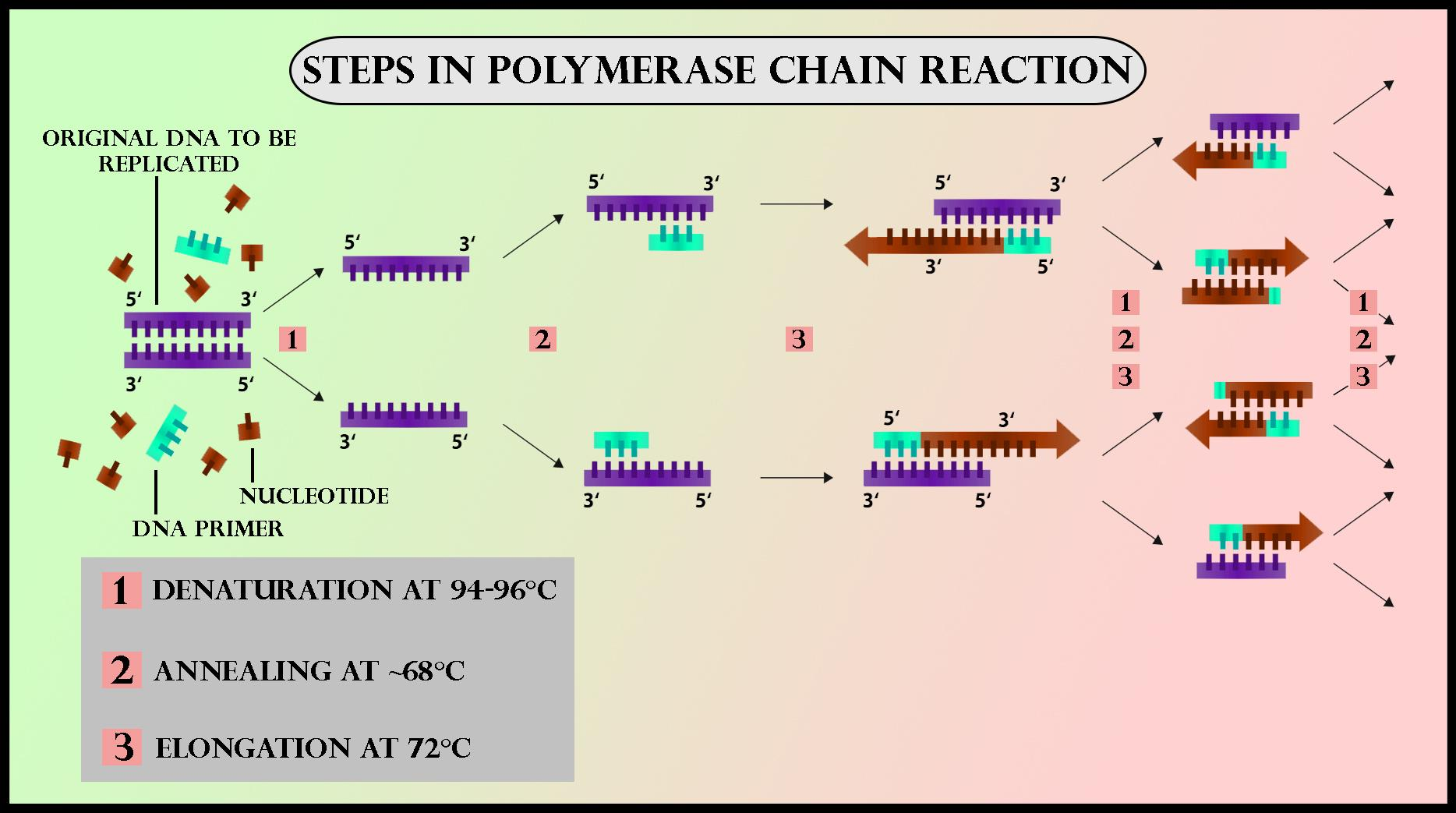
What Are The Three Main Steps In The Pcr Process slide share
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Key Principles
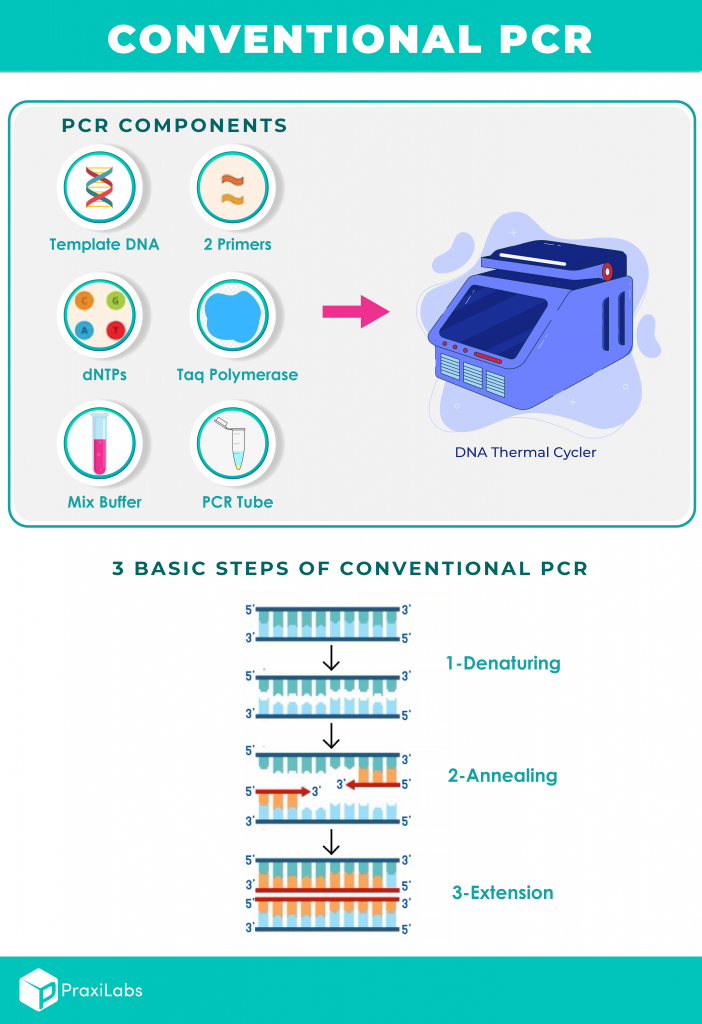
What Are The Three Basic Steps of Conventional PCR? PraxiLabs
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing steps of PCR?
Types of PCR Common Kinds of Polymerase Chain Reaction BioMadam
PCR Overview GoldBio
Related Post: