Template Strand Mrna
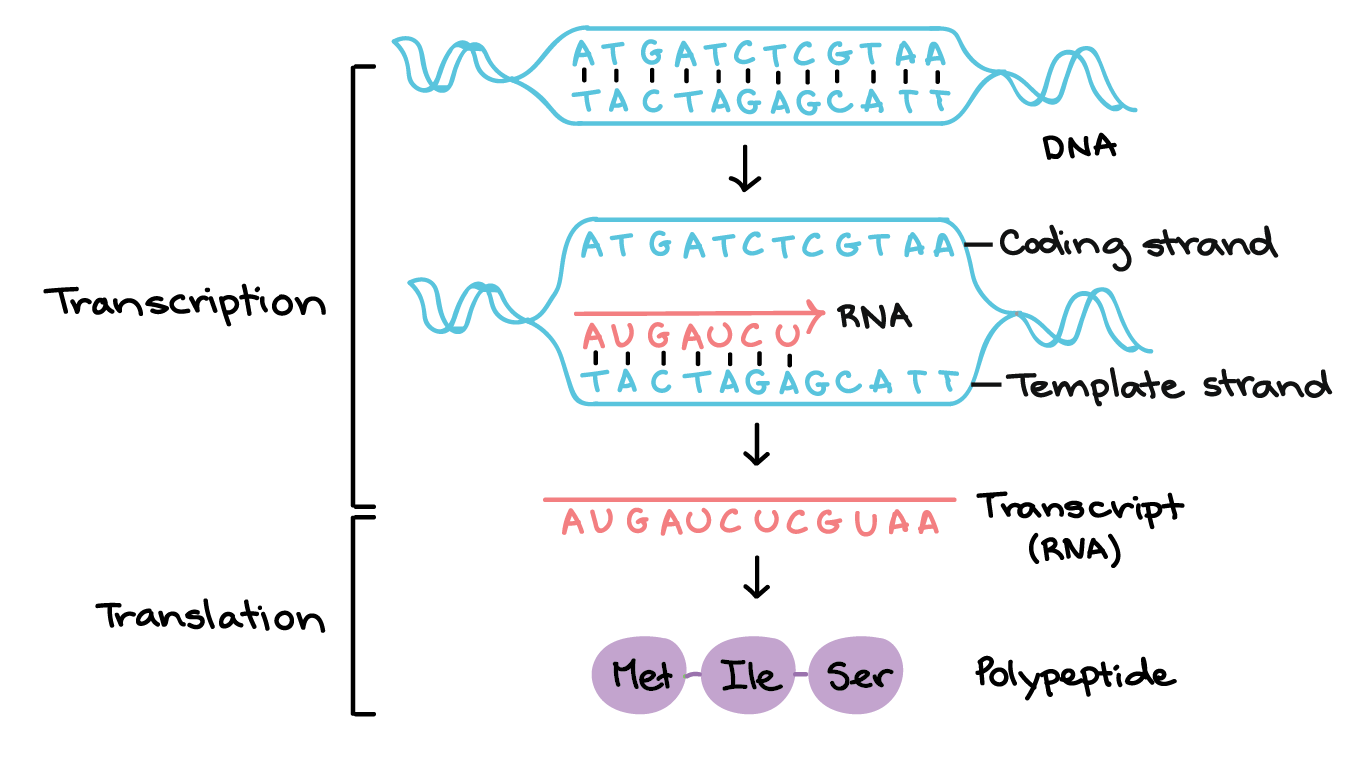
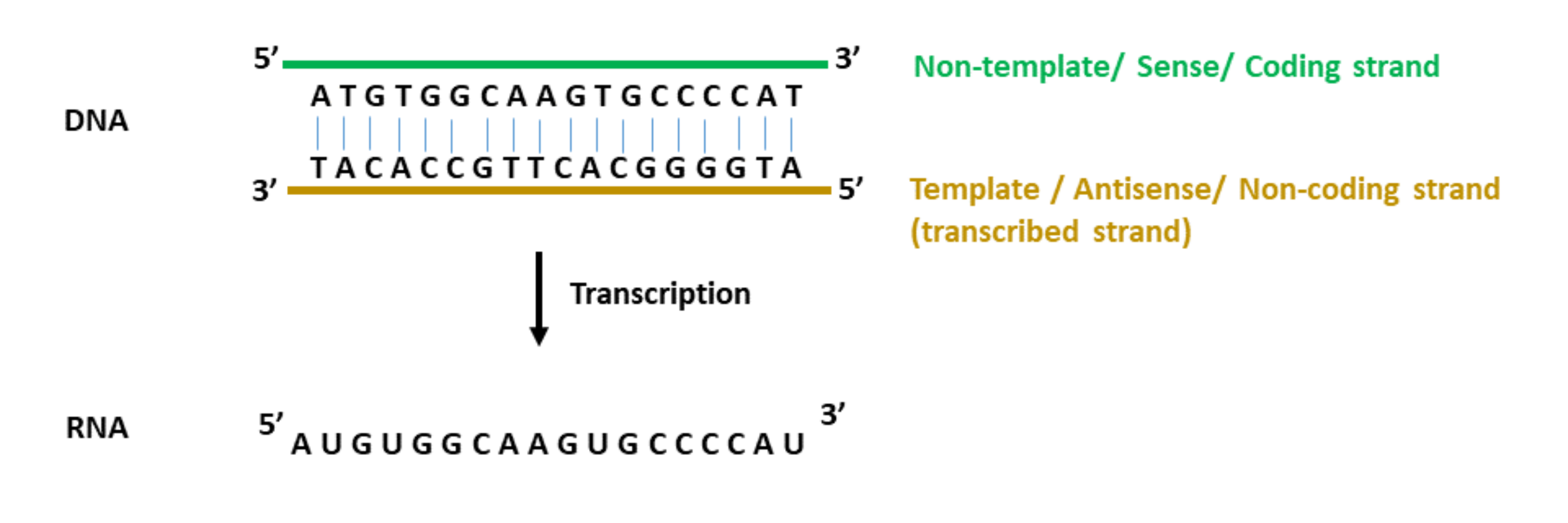
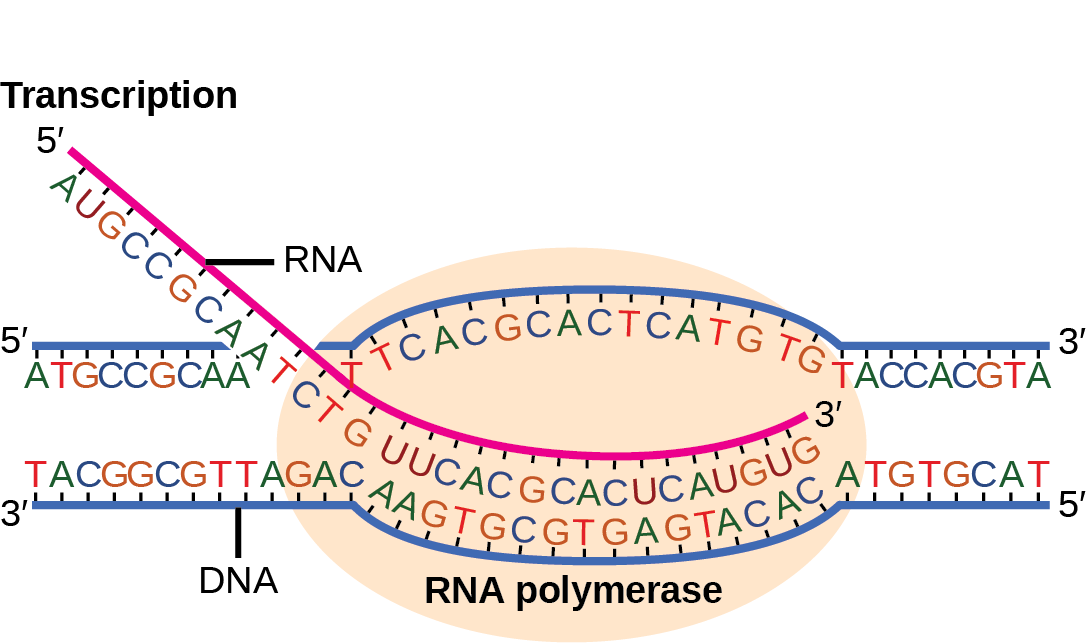
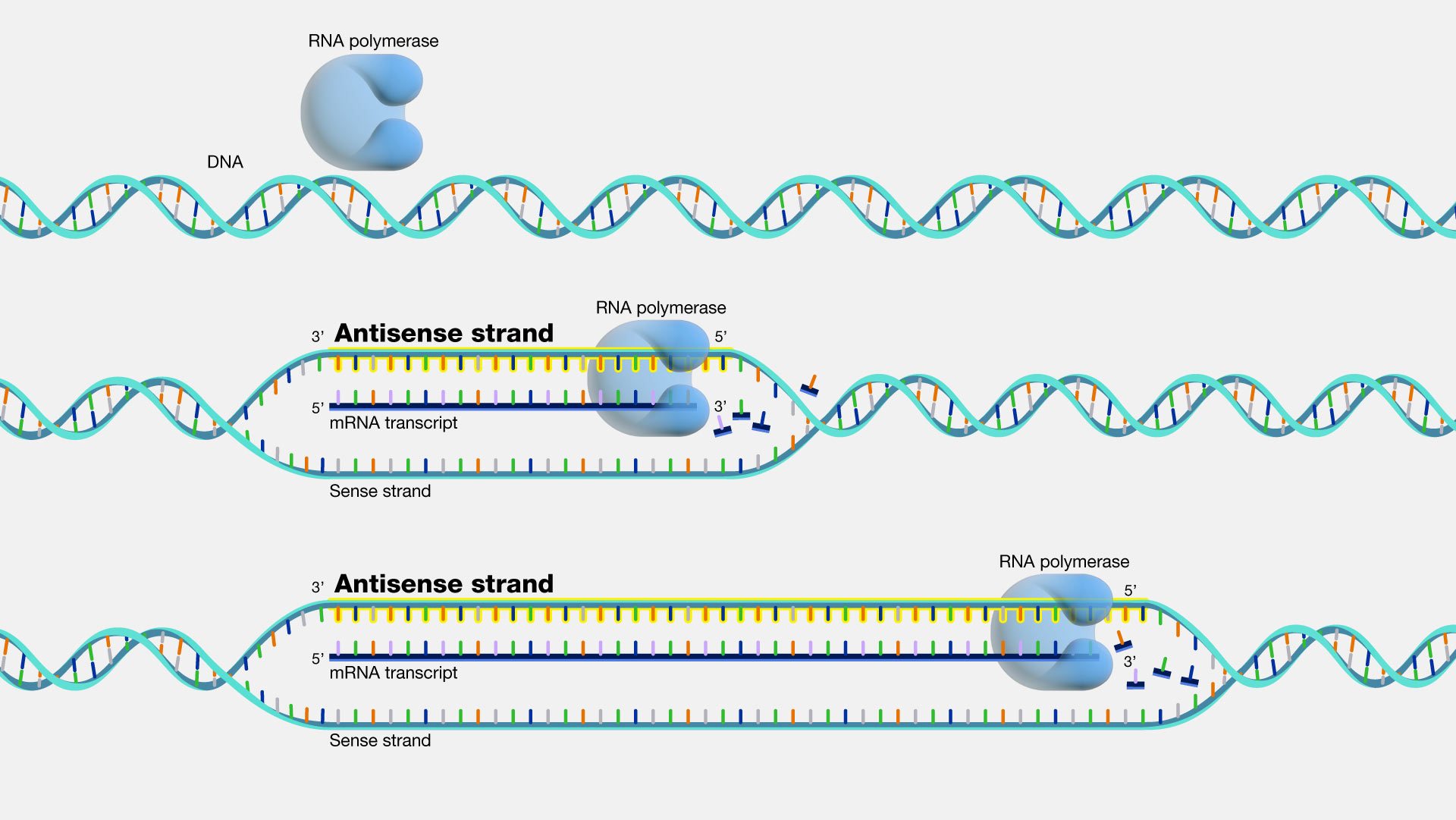
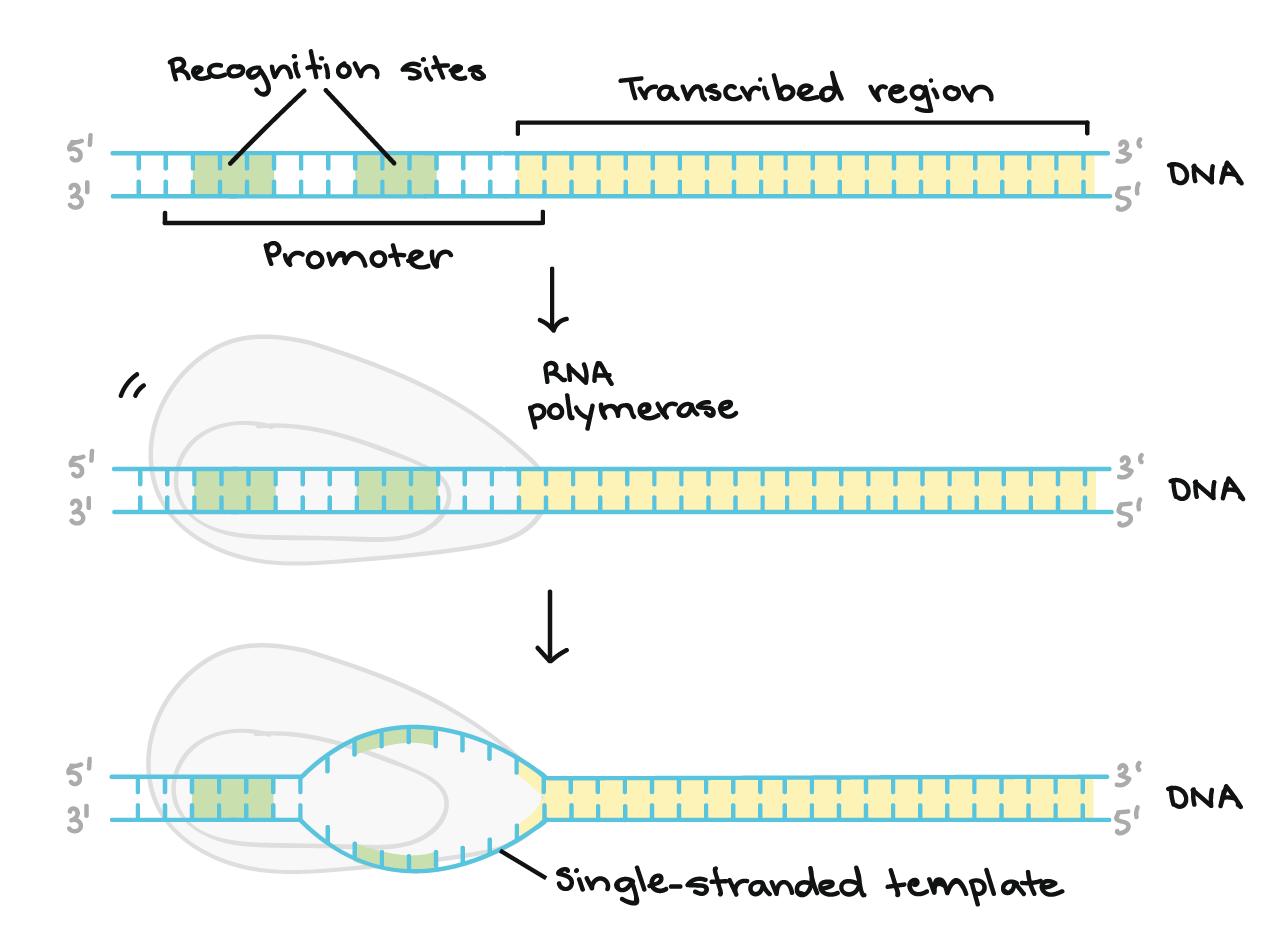
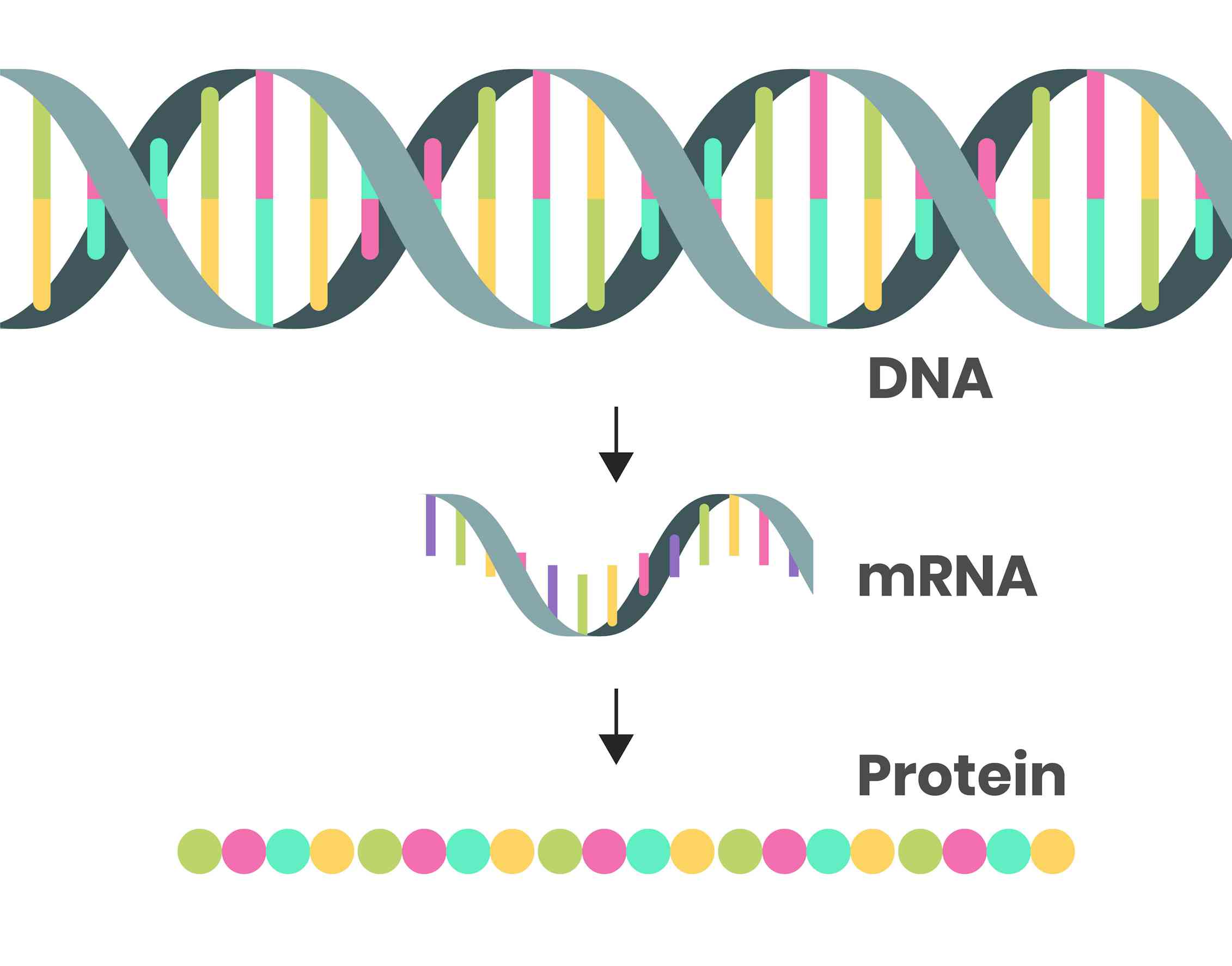
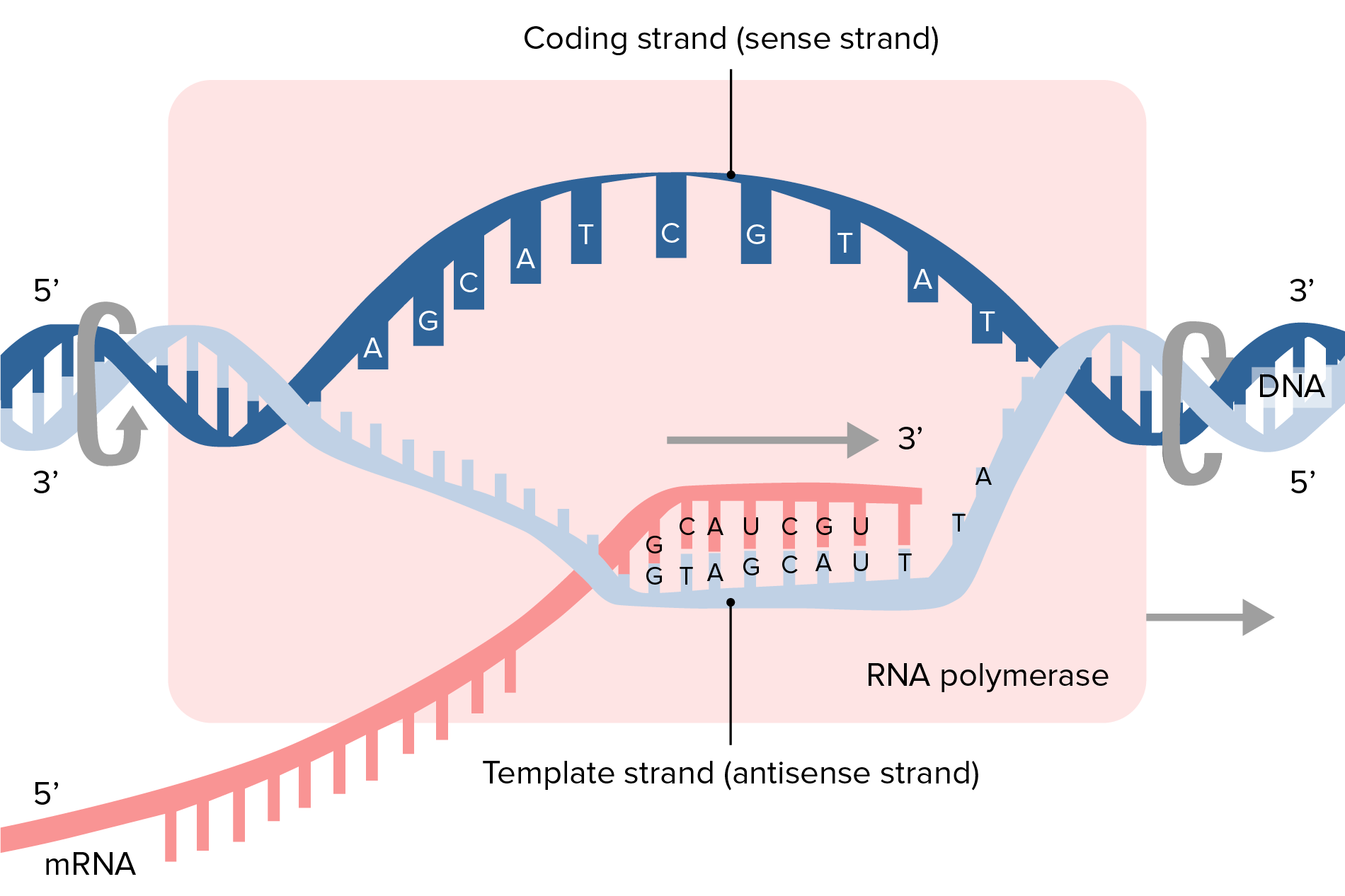
Template Strand Mrna - The template strand is the top strand; Web the transcribed dna strand is called the template strand, with antisense sequence, and the mrna transcript produced from it is said to be sense sequence (the complement of. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is. Asked mar 3, 2017 at 0:17. Web these are displayed from left to right, namely, in the direction in which the mrna would be synthesized (5' to 3' for the mrna) antiparallel to the dna coding strand. The section shown is part of a protein coding gene. That half of a double helix that is read by polymerase enzymes during transcription or dna replication. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. It is also known as. Web the template strand is one of the dna strands whose base sequence helps in building mrna through complementary base sequencing. Web below is a section of double stranded dna. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web these are displayed from left to right, namely, in the direction in. The template strand is recognized by dna. Web template strand which is also known as antisense strands runs in the direction of 3’ to 5’ ends, which runs opposite to the coding strands. That half of a double helix that is read by polymerase enzymes during transcription or dna replication. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna. Asked mar 3, 2017 at 0:17. That half of a double helix that is read by polymerase enzymes during transcription or dna replication. The template strand is recognized by dna. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. The coding strand is the bottom strand. Learn about this topic in these articles: Web template strand which is also known as antisense strands runs in the direction of 3’ to 5’ ends, which runs opposite to the coding strands. Web below is a section of double stranded dna. It is also known as. It carries the gene complementary to one strand of the dna. Web translates dna or mrna to the other and a protein strand (amino acids). Web the dna strand that mrna is built from is called the template strand because it serves as a template for transcription. Web the template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Template strand or “ antisense. It. Web these are displayed from left to right, namely, in the direction in which the mrna would be synthesized (5' to 3' for the mrna) antiparallel to the dna coding strand. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. The coding strand is the bottom strand. The coding strand determines the correct. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. The section shown is part of a protein coding gene. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web these are displayed from left to right, namely, in the direction in which the mrna would be synthesized (5' to 3' for the mrna) antiparallel to the dna coding strand.. Web the template strand is one of the dna strands whose base sequence helps in building mrna through complementary base sequencing. This is called the template strand, and the rna molecules produced are. The template strand is recognized by dna. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used. Web the template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. It is also known as. This is called the template strand, and the rna molecules produced are. Template strand or “ antisense. It is also known as. Web template strand which is also known as antisense strands runs in the direction of 3’ to 5’ ends, which runs opposite to the coding strands. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is. Template strand or “ antisense. The coding strand is the bottom strand. That half of a double helix that is read by polymerase enzymes during transcription or dna replication. Web these are displayed from left to right, namely, in the direction in which the mrna would be synthesized (5' to 3' for the mrna) antiparallel to the dna coding strand. It is also called the antisense strand. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. Web the dna strand that mrna is built from is called the template strand because it serves as a template for transcription. This is called the template strand, and the rna molecules produced are. Web the transcribed dna strand is called the template strand, with antisense sequence, and the mrna transcript produced from it is said to be sense sequence (the complement of. A dna molecule is double stranded. Web the copying of dna to mrna is relatively straightforward, with one nucleotide being added to the mrna strand for every complementary nucleotide read in the dna strand. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Web translates dna or mrna to the other and a protein strand (amino acids). It carries the gene complementary to one strand of the dna. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web the template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. The template strand is recognized by dna. Learn about this topic in these articles: The section shown is part of a protein coding gene.What strand of DNA is used to make a complementary copy or to make a
Common misconceptions in biology Making sense of the sense and
Heredity DNA Structure, Composition, Britannica
Biology 2e, Genes and Proteins, Prokaryotic Transcription
Antisense
Information Flow and Levels of Regulation Medical 1st Ed
Genes to proteins Central Dogma BIO103 Human Biology
What is mRNA? The messenger molecule that's been in every living cell
Protein Synthesis Anatomy and Physiology I
RNA Types and Structure Concise Medical Knowledge
Related Post: