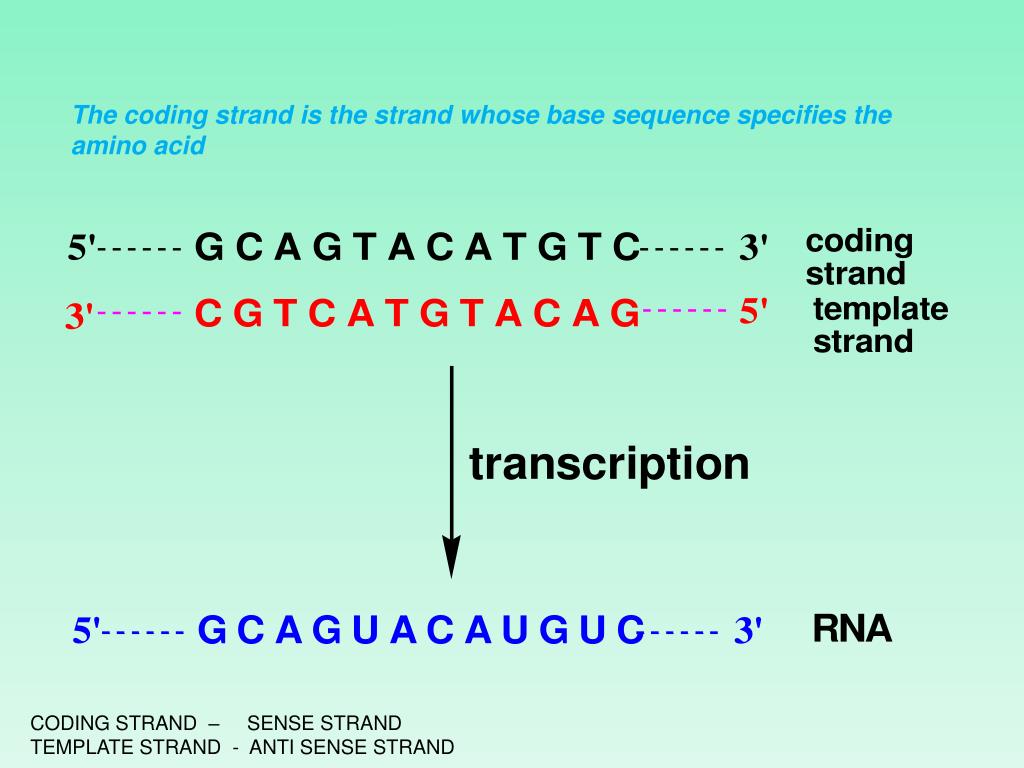
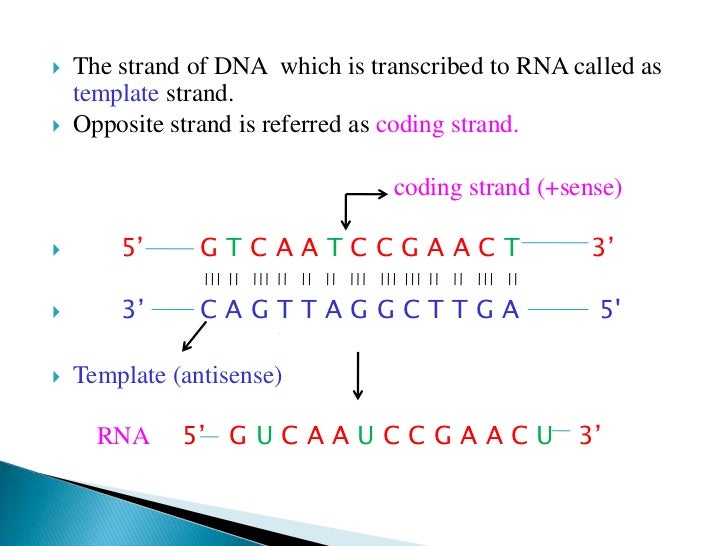
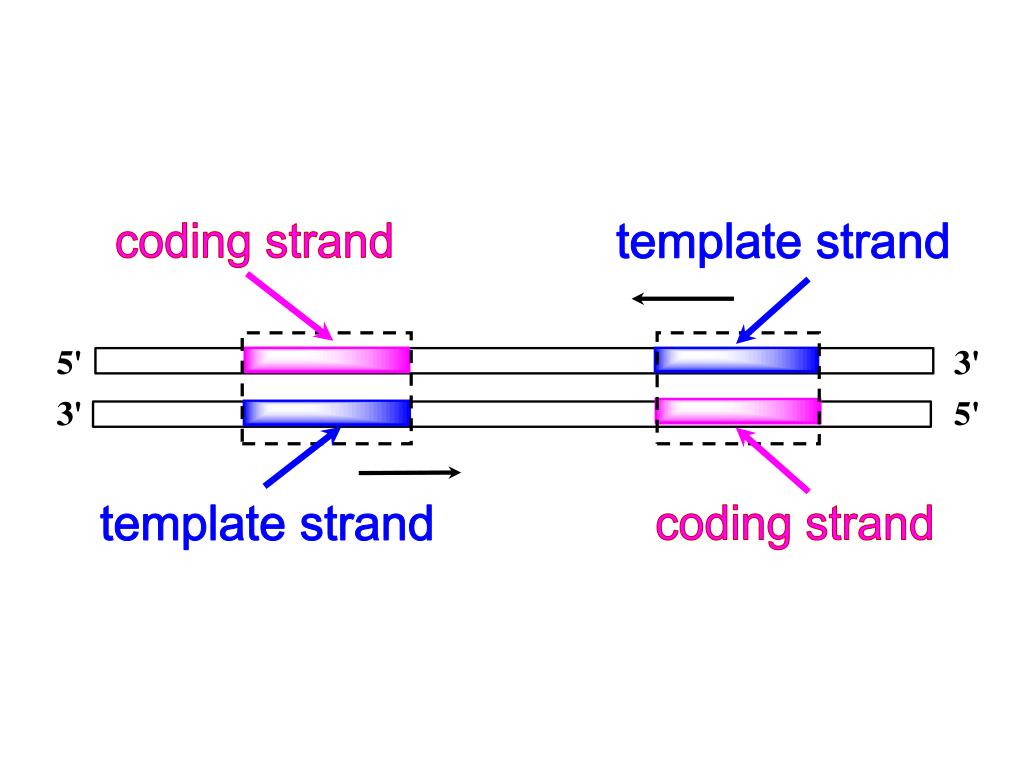
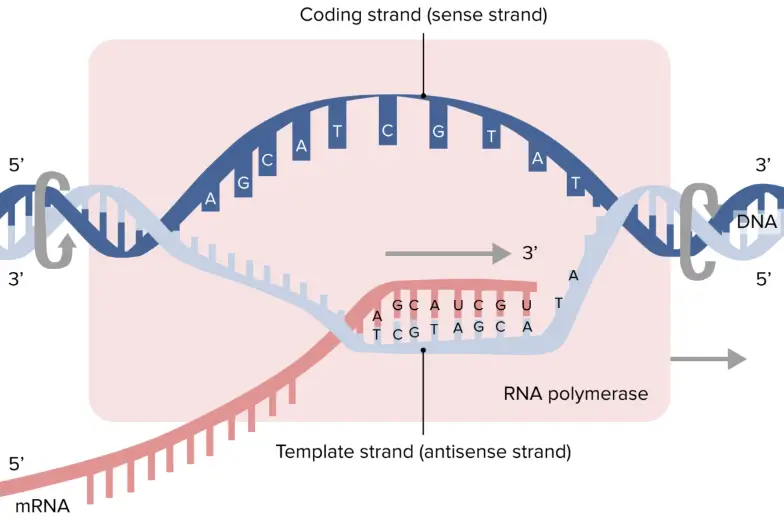
Template Strand Coding Strand
Template Strand Coding Strand - Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. Web template and coding strands are the terms generally used to describe the strands which are present in the dna. Template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. Web this template strand is called the noncoding strand. Importance in dna replication both the coding strand and the template strand are vital for the process of dna replication, which ensures the accurate duplication of genetic information during cell. Considering the same dna sequence:. A always pairs with t, and g with c. The other strand of dna (the coding strand or sense strand) is not normally used as a template for transcription. Here are some features of codons: Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. It serves as the blueprint for mrna formation, guiding its synthesis. Web key differences between template and coding strand. Web the coding strand turns gray and then disappears, leaving the template strand (see strands above ). Web the template strand, also known as the antisense or minus strand, is instrumental. There are a few assumptions you can make. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription. Often termed as the antisense strand or minus strand. Web the template strand, also known as the antisense or minus strand, is instrumental in rna synthesis. This template strand walks in the direction of 3’ to 5’. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web key differences between template and coding strand. Template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Understanding the differences between these two strands is. Its sequence is used as a template during transcription to produce an rna molecule. Template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. During the process of transcription, one of the two strands in the double stranded dna serves as a template strand. Web this template strand is called the noncoding strand. There are a few assumptions you can. Web the coding strand serves as a template for the rna polymerase, which ensures that the rna strand is complementary to the coding strand. Most codons specify an amino acid three stop codons mark the end of a protein one start codon, aug, marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine The nontemplate strand is. The coding strand, alternatively termed the sense or plus strand, is paramount in determining the accurate nucleotide sequence for mrna during transcription. Most codons specify an amino acid three stop codons mark the end of a protein one start codon, aug, marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine Orfs are sequence segments that begin. Template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. You have the sequence of template strand , that means you have non coding strand. It's complementary strand would be coding strand as i've attached in the picture below. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. It is also known as sense. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web the coding strand is directly involved in protein synthesis, while the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis. During the process of transcription, one of the two strands in the double stranded dna serves as a template strand. This pairing is indispensable for accurate replication and transcription.. It's complementary strand would be coding strand as i've attached in the picture below. Non coding / template/ antisense are all same. This pairing is indispensable for accurate replication and transcription. The coding strand is the bottom strand. Given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat. There are a few assumptions you can make. A always pairs with t, and g with c. Template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Most codons specify an amino acid three stop codons mark the end of a protein one start codon, aug, marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine Considering. The coding strand, alternatively termed the sense or plus strand, is paramount in determining the accurate nucleotide sequence for mrna during transcription. The other strand of dna (the coding strand or sense strand) is not normally used as a template for transcription. Template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Considering the same dna sequence:. Web messenger rna is transcribed using only one dna strand as the template. Here are some features of codons: It has the same sequence (except for t for u substitutions) as the mrna. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. It serves as the blueprint for mrna formation, guiding its synthesis. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Web the section shown is part of a protein coding gene. Web this template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Web codons cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. The coding strand, also called the sense strand or the plus strand, is a crucial component of the dna molecule. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand [1] [2]) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil ). Most codons specify an amino acid three stop codons mark the end of a protein one start codon, aug, marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine The mrna produced is consequently sense rna. There are a few assumptions you can make. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription.Difference Between Template and Coding Strand
Template Strand Vs Coding Strand Understanding The Difference GRAPHICOLD
Coding Versus Template Strand
PPT Transcription PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3154392
Transcription
Template and coding strand targeting of spacers. A Schematic
PPT Chapter 11 Transcription PowerPoint Presentation, free download
DNA Transcription Steps and Mechanism • Microbe Online
Dna Templating
Difference between Sense Strand and Antisense Strand of DNA Dna
Related Post: